Preventing Static Defects in Digital Printing
- Published: April 07, 2025
By Dr. Kelly Robinson, Founder, Electrostatic Answers
Digital printing has revolutionized document creation. Carbon copies (.cc) are things of the past! The digital printing revolution has come with new challenges. For example, static charges can cause defects in digital printing in several ways. To see how to prevent these problems, let’s take a closer at how static charges can cause defects in Inkjet Printing and Thermal Transfer Printing.
The Inkjet Printhead in Figure 1 ejects small Ink Droplets that land on the Receiver Sheet to form the Printed Image. The Ink Droplets must be ejected at just the right time and follow a precise path to the Receiver Sheet. Smaller droplets are needed for higher quality images.
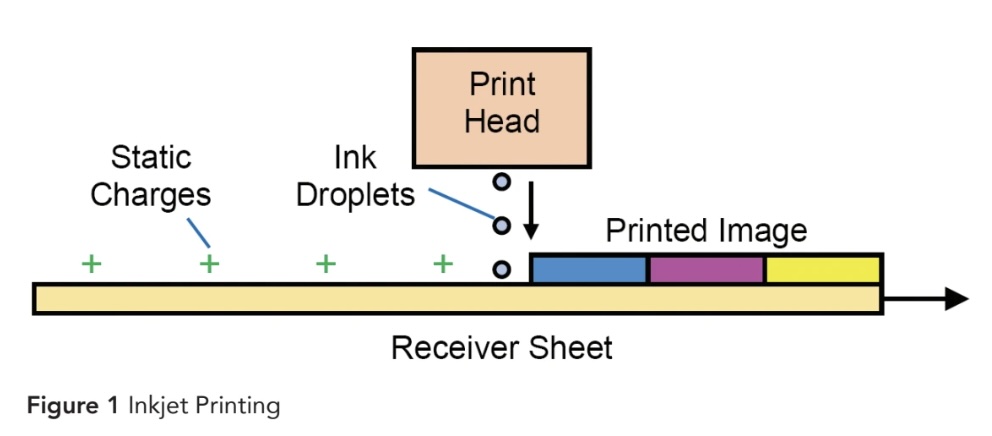
Static charges on the Receiver Sheet can cause printing defects in several, different ways.
Static Sparks - Before reaching the Printhead, static sparks on the Receiver Sheet can change the surface energy of the Receiver Sheet just like a corona treater. When an Ink Droplet reaches the receiver sheet, the liquid ink spreads differently in areas where sparks occurred, which causes image defects.
Prevent this defect by suppressing static sparks along the path from the Receiver Sheet supply to the Printhead. Use best practice static control methods.
Ink Spreading - After an ink droplet lands, static charges on the Receiver Sheet can cause the liquid ink to flow and spread in the wrong direction causing a defect. Prevent this defect by neutralizing static charges on the Receiver Sheet just before it reaches the Printhead.
Charged Droplets - Static charges on the Receiver Sheet under the Printhead can induce electrical charges on the Ink Droplets as they form. Electrical charges on the Ink Droplets change the trajectory of the droplets so that they deposit in the wrong locations on the Receiver Sheet. Droplets that land in the wrong place cause image defects. Prevent this defect by neutralizing static charges on the Receiver Sheet just before it reaches the Printhead.
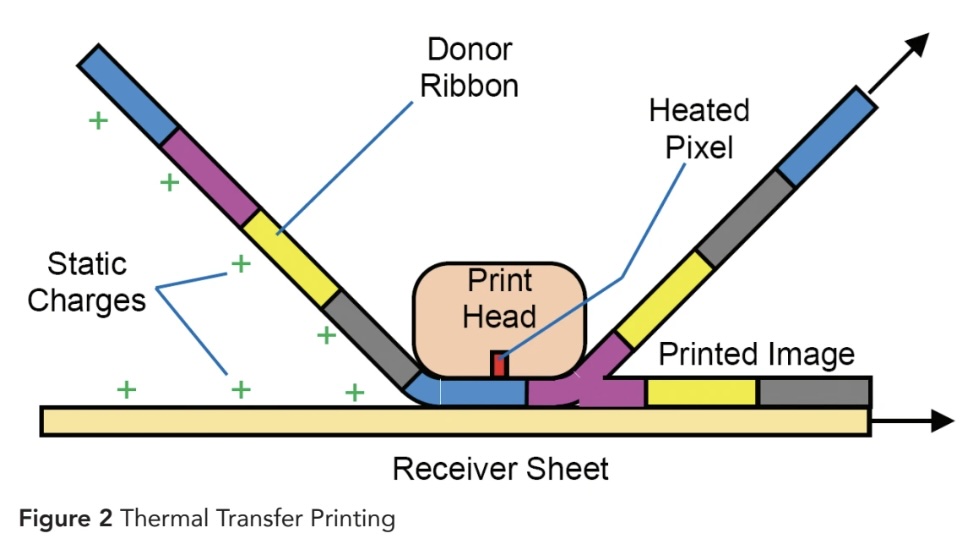
The Thermal Transfer Printhead in Figure 2 has many, small Heated Pixels. When the Heated Pixel is hot, dye from the Donor Ribbon transfers to the Receiver Sheet forming a dot. The Heated Pixels must be turned on at just the right times for print an image.
Smaller Heated Pixels are needed for prints higher quality images. The Donor Ribbon must be in good contact with the Print Head and with the Receiver Sheet for dye to transfer properly.
Static charges on the Donor Ribbon and on the Receiver Sheet can cause printing defects in several different ways.
Sparks to the Printhead - Static charges on the Donor Rib bon in Figure 2 can cause sparks to the Print Head. A small spark can cause a logic error that causes a printed defect. This is a "soft failure" meaning that the system can recover.
A larger spark can physically damage the Headed Pixels in the Print Head. The damaged Heated Pixels fail to operate properly causing printed defects. This is a "hard failure" meaning that the Print Head must be replaced to solve the problem.
Prevent sparks by neutralizing static charges on the Donor Ribbon before it reaches the Printhead. Use best practice static control methods to neutralize static charges. The area from the Donor Ribbon supply to the Printhead is congested. There is usually little room for a powered static dissipater. Use a passive dissipater because they are smaller and will likely fit. Avoid static brushes and tinsel because the fibers can break causing contamination problems. Use ionizing cords or ionizing rods to minimize contamination.
Donor Ribbon Sticking - Static charges on the Donor Ribbon in Figure 2 can cause it to stick to the Print Head. Donor Ribbon sticking to the Printhead is complicated. Contaminates on the Donor Ribbon accumulate on the Print Head causing sticking. A stuck Donor Ribbon causes printed defects. Static charges on the Donor Ribbon make things worse.
To recover from a stuck Donor Ribbon, it must be cleared and the Print Head must be cleaned. To help prevent sticking, neutralize static charges on the Donor Ribbon before it reaches the Print Head. Use best practice static control methods.
Static charges on the Receiver Sheet can also cause Donor Ribbon sticking. To help prevent sticking, neutralize static charges on the Receiver Sheet before it reaches the Print Head. Use best practice static control methods.
Static charges can cause digital printing defects in several different ways. Prevent these problems by neutralizing static charges on the receiver sheets before they reach the Print Head. For Thermal Printing, neutralize static charges on the Donor Ribbon before it reaches the Print Head.
About the Author
Dr. Kelly Robinson writes on static issues occurring in converting processes. Robinson founded Electrostatic Answers, has 40-plus years’ experience in industrial problem solving and was named Top Manufacturing Consulting Services Provider 2023 by Managing MFG. He can be reached at Kelly.Robinson@ElectrostaticAnswers.com.