Featured Stories
-
The Importance of Roll Cleaning and Maintenance
A question-and-answer with Joe Walczak, President of Sonic Solutions. -
Leveraging New Technology for Advancements in Battery Electrode Manufacturing
Machine designers and process engineers in the battery industry are witnessing a pivotal shift towards more space-efficient, precise and... -
Advantages of Shear, Razor and Crush Web Slitting Techniques
When choosing a slitting method, many factors must be considered, including interaction with inspection systems.
News | New Products
-
GMG Color Americas to showcase next-generation color management solutions at FTA FORUM & INFOFLEX 2025
GMG Color, a global leader in color management and proofing solutions, announces its participation in the FTA FORUM & INFOFLEX 2025
-
Kongsberg Precision Cutting Systems Launches IPC 3.1 For Faster, Smoother Table Operations
Kongsberg Precision Cutting Systems (PCS) has launched the latest version of its table operating software IPC 3.1.
-
EFI Showcases Latest Solutions Expanding the Possibilities of Digital Printing at the ISA International Sign Expo
Electronics For Imaging, Inc. (EFI™) is showcasing its newest hybrid and flatbed LED inkjet printers at the ISA International Sign Expo® in Las Vegas, April 23-25.
-
EMT International Expands Cutting Technology Portfolio with slittec Partnership
Strategic Alliance Enhances EMT's Comprehensive Slittling Solutions for Paper, Film and Packaging Industries
-
BW Converting Highlights Hudson-Sharp Pouch Machines at Petfood Forum 2025
Driving innovation in pet food packaging with high-performance bag and pouch converting machines
-
Mark Andy Sponsors 2025 Phoenix Challenge College Competition Advancing Workforce Development and Industry Engagement
Mark Andy, a global printing and labels solutions company, continues its support of the Phoenix Challenge
-
Cards & Systems Solutions Invests in Rollem InsigniaX3 to Expand In-House Die-Cutting Production
Cards & Systems Solutions, a leader in the manufacturing of plastic cards and comprehensive fulfillment services, has received a successful installation of the Rollem InsigniaX3 Rotary Die Cutter.
Expert Advice
Static Beat | Static Dissipator Locations
- Published: September 18, 2014, By Kelly Robinson
 Static must be controlled sufficiently to suppress sparks. Static charges on plastic and paper webs cause sparks that can ignite flammable solvent vapors and shock operators who must handle the wound rolls. These sparks also deposit spots of charge that can cause cut sheets to stick.
Static must be controlled sufficiently to suppress sparks. Static charges on plastic and paper webs cause sparks that can ignite flammable solvent vapors and shock operators who must handle the wound rolls. These sparks also deposit spots of charge that can cause cut sheets to stick.
Many static dissipators are commercially available. Passive dissipators, such as static brushes, grounded pin arrays, and tinsel, can reduce a high level of static charge to a low level. And active static bars can reduce the static level to essentially zero. Excellent technology for dissipating static charge is available. The challenge is to install dissipators in the right places so that sparks are suppressed.
When identifying locations for static dissipators, think in terms of RISKS and COUNTER-MEASURES. Use the two-step process in Figure 1 to identify locations for your static dissipators. The first step is to identify areas at RISK from static sparks, such as C1D1 solvent areas and winding rolls. Any area of the process where sparks could cause injury, downtime, or product quality problems are RISKS. Our “Inner Circle” static dissipators are be installed to suppress sparks in RISK areas.
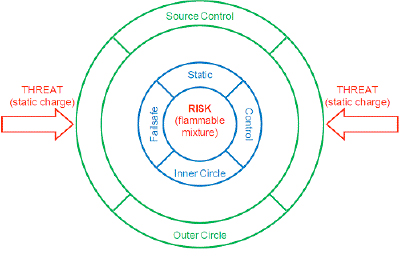
The second step is to identify charging sources using a static survey. Use an electrostatic fieldmeter to measure static on each accessible web span. The electric field on the web span exiting a particular roller or process that is a charging source is significantly higher than the electric field measured on the entering web span.
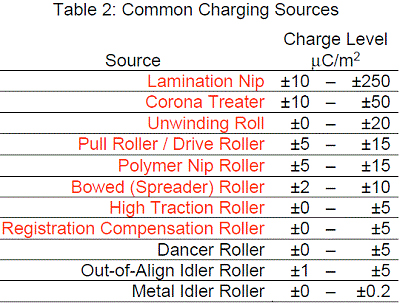
Common charging sources in Table 2 listed in red deposit enough static on a web to cause sparks. Sources that deposit ±5 μC/m2 of static charge cause the electric field to increase by ±6 KV/cm and sparks can occur. Our “Outer Circle” static dissipators are installed to dissipate static from each source of static charging.
RISK areas in Figure 3 are protected by “Inner Circle” static dissipators and static from each charging source is dissipated by “Outer Circle” dissipators. With static dissipators installed in these locations, our RISK areas are protected from static charge THREATS by a fault tolerant static control system. The failure of any single dissipator (Fault) is insufficient to expose the RISK to a THREAT.
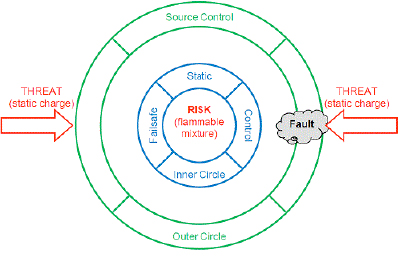
Commercially available static dissipators have excellent performance. Our challenge is to install these static control devices to suppress sparks in RISK areas of our process. Static dissipators should be installed “best practice” locations to protect RISK areas with a fault tolerant static control system so that any single failure or fault is insufficient to expose a RISK to a static THREAT.
I invite you to ask questions about this column and to suggest future topics. My email address is: Kelly.Robinson@ElectrostaticAnswers.com.
Static control expert Dr. Kelly Robinson, president of Electrostatic Answers, has 27+ years of experience in problem-solving and consulting. Kelly writes PFFC's Static Beat column and the Kelly on Static blog. Contact him at 585-425-8158; kelly.robinson@electrostaticanswers.com; www.electrostaticanswers.com.